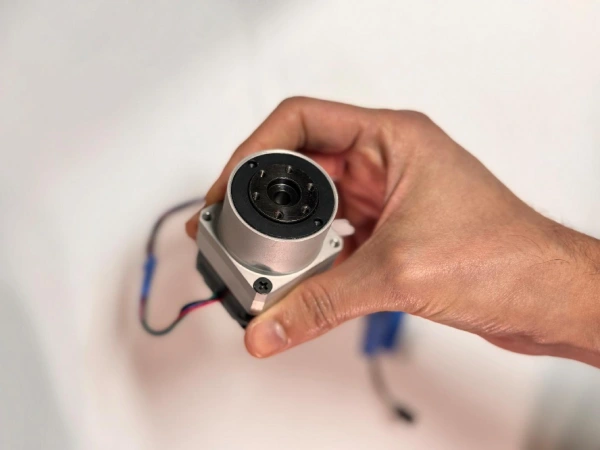
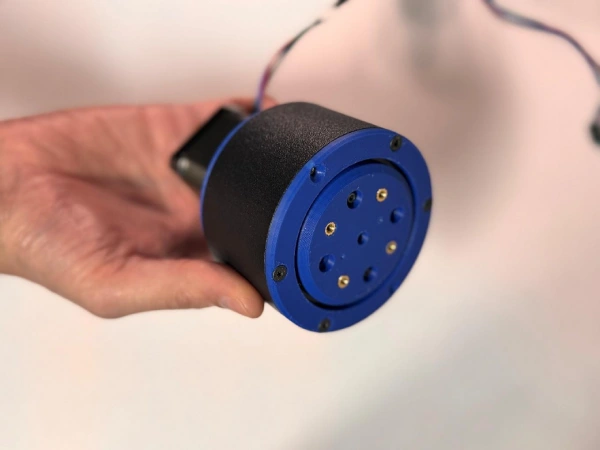


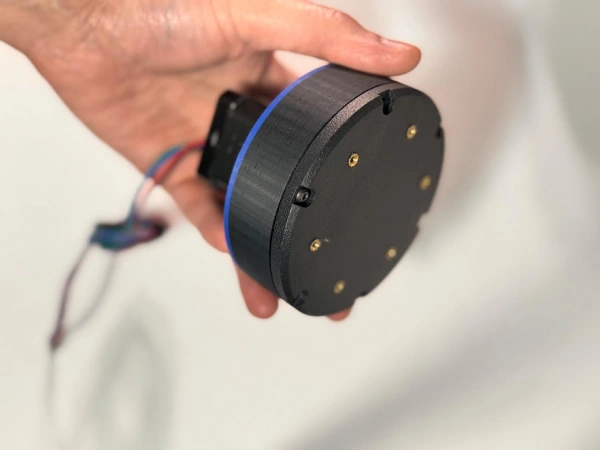

I used the online Harmonic Drive Simulator to generate and download the teeth profile. One important note is that harmonic drives do not have standard involute gear teeth profile. The teeth have a trapezoidal profile described in the original patent, US 2,906,143.
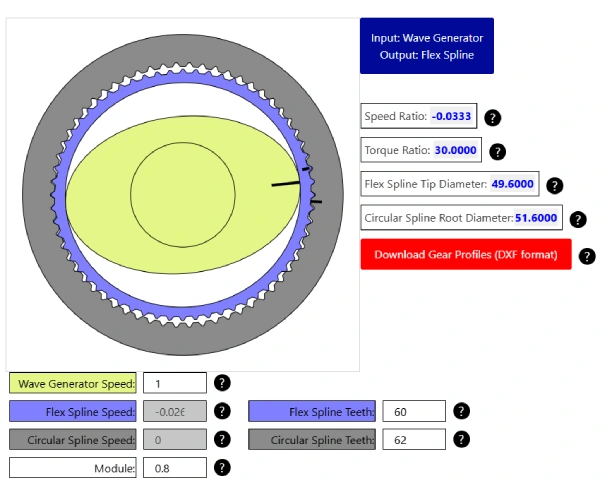
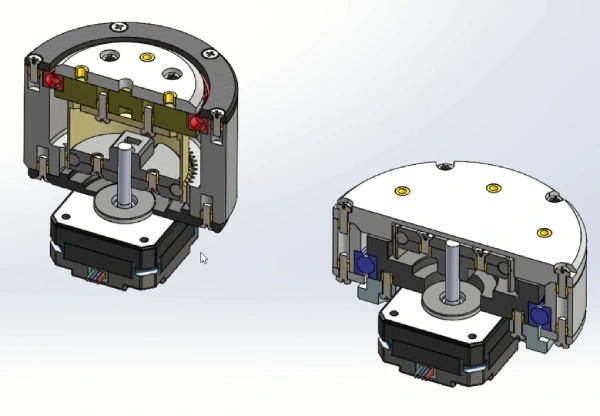
Once I had the teeth profile, I decided to create two designs: cup and pancake harmonic drives. The difference is mainly due to the design of the flexspline. In both cases the flexspline is the output of the drive, however, for the pancake harmonic drive, the flexspline is coupled to a third gear. This allows the design to be more compact.
I first measured the torque of the Nema17 stepper motor. This can later be used to calculate the efficiency of the harmonic drives.
Using a force gauge, I measure a torque output of 0.24 Nm.
To measure the torque of the harmonic drives I used a torque wrench adapter with a resolution of 0.01 Nm.
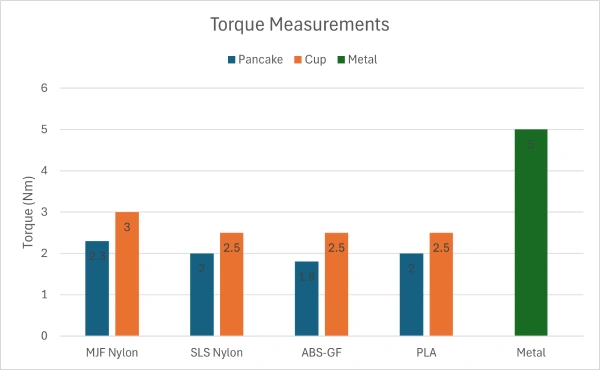
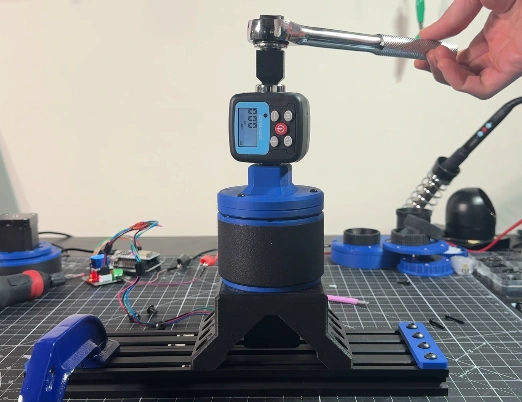
I tested the harmonic drives with different flexspline materials: MJF Nylon, SLS Nylon, ABS-GF and PLA.
The key conclusions we can make is the best performers are the cup-style harmonic drive with an MJF Nylon flexspline. One important note is that all these measurements were done without any lubrication.
We can also note that the metal harmonic drive is much more efficient, which is expected due to lower friction and tighter manufacturing tolerances.
To measure the backlash I used a drop gauge and a lever length of 0.15 m.
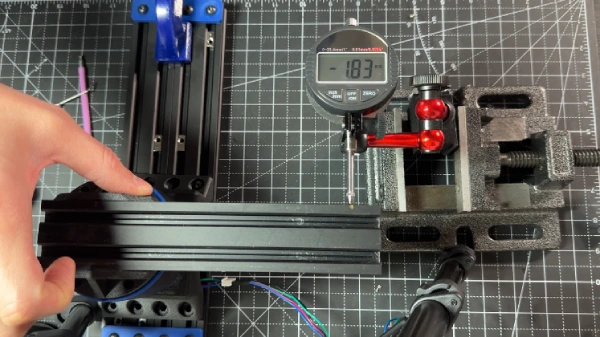
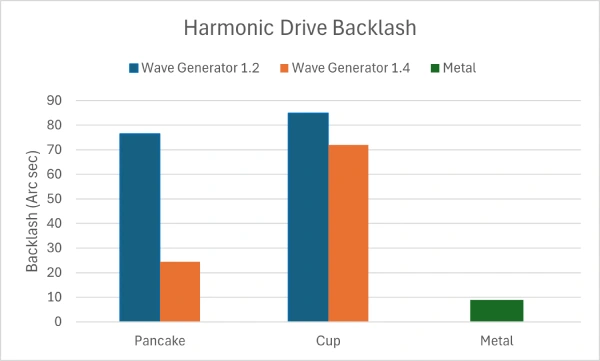
Fortunately, we can easily improve the backlash performance by increasing the compression on the flexspline. To do this, I 3D printed a second larger wave generator. However, as shown later, this will be at the expense of torque efficiency.
Results show that the larger wave generator allows backlash improvement, however, it is still far from the metal harmonic drive.
As a conclusion we can say that 3D printed harmonic drives are clearly not as efficient as metal harmonic drives. They do not provide the same level of torque output or backlash. However, they might still be suitable for applications that do not require high torques.
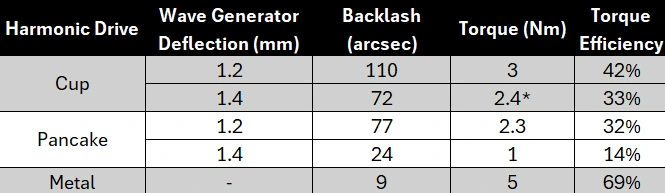
*2.8 Nm when using lubrication
One example might be a SCARA robot. These types of robots do not require high torque motors as most of the load is radial due to the moment arm.
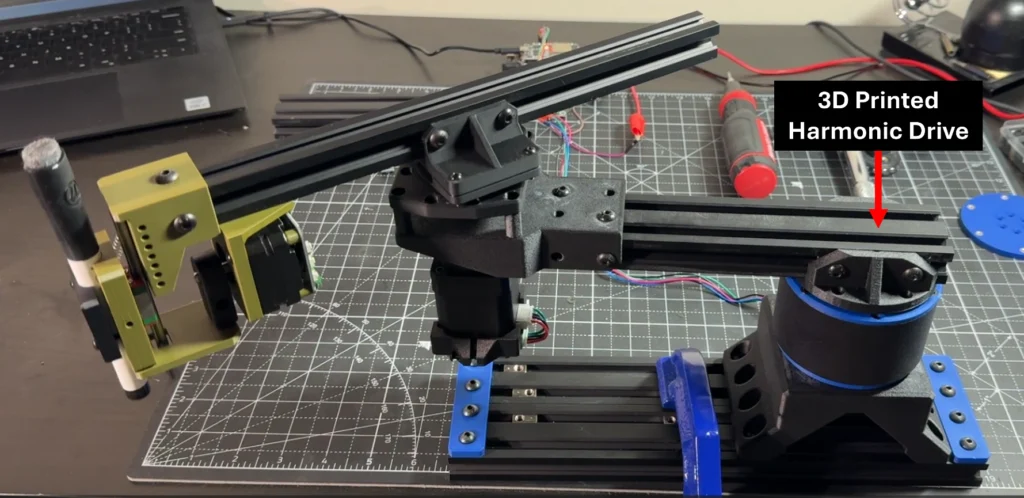

If you would like to see more details about the design process of these harmonic drives, feel free to check the Youtube videos.
© Me Vertuoso All Rights Reserved 2025